Prof. Lior Appelbaum
Research
Sleep and sleep disorders:
Sleep is an evolutionarily conserved process that is vital for animal survival. Sleep disturbances affect a large portion of the general population and represent a major health burden. Although sleep clearly improves brain performance, the function of sleep is unclear. We have characterized sleep, cloned sleep genes, visualized sleep circuits, and established zebrafish models for sleep disorders. We also found that sleep enable efficient nuclear maintenance of single neurons.
Neurodevelopmental disorders:
Neurodevelopmental disorders are characterized by cognitive, social, and motor deficits. The cause for these disorders is often genetic mutations that can lead to alteration in genetic pathways, neurogenesis, myelination, synaptic plasticity, and the activity of neural circuits. We established several zebrafish models for neurodevelopmental and endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism, fragile-x-syndrome, narcolepsy and epilepsy. These models are used to identify and characterize the genetic, neural and behavioral mechanisms of the disorders, and to test potential genetic and pharmaceutical treatments.
Nerves, evolution and behavior in cnidarians:
We study the evolution and function of the nervous system in the ancient cnidarians (i.e. corals, jellyfish and sea anemone). We combine lab and field experiments, and use molecular and behavioral techniques to understand how a simple nerve net regulates behavior such as sleep.
Specific projects
Why do we sleep? Live imaging of the cellular mechanisms of sleep
Prolonged sleep deprivation can be lethal, and sleep disturbances are associated with various deficiencies in brain performance. However, how sleep affect the function of single neurons is unclear. We developed a technique to visualize single molecules in individual neurons of live awake and sleeping zebrafish. Using this approach, we found that sleep increases the movement of chromosomes (chromosome dynamics), which alters their structure to enable reduction of DNA damage, while neuronal activity has the opposite effect. Thus, chromosome dynamics can be a marker to define individual sleeping neurons, and one of the roles of sleep is to perform nuclear maintenance. The current research focus on nuclear and cellular mechanisms of sleep.
Sleep disorders and the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus regulates fundamental brain functions, such as reproduction, metabolism and sleep. The hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin (Hcrt) neurons are regulators of feeding, emotions, reward, sleep and wake, and Hcrt neuron deficiency results in the sleep disorder narcolepsy in humans and animal models. We established a transgenic zebrafish model, enabling inducible ablation of Hcrt neurons, as a model for narcolepsy. Using combination of RNA-seq, live-imaging, and behavioral experiments, we identify and characterize novel hypothalamic and Hcrt-neuron-specific genes in zebrafish. In addition, we study structural and functional connection between several neuropeptide-producing hypothalamic neuronal networks such as Hcrt, and neurotensin (Nts).
Sleep and synaptic plasticity
Sleep is conserved in evolution, and similar circadian and homeostatic factors regulate sleep in animals as distantly related as worms, flies, fish, and humans. Accumulating evidence shows that sleep is important for synaptic plasticity, memory, and learning. Using time-lapse two-photon imaging of excitatory and inhibitory pre- and post-synaptic markers, we study circadian and homeostatic control of rhythmic synaptic plasticity in the brain of live zebrafish.
Fragile X syndrome
Fragile-X syndrome (FXS) is the most common single-gene inherited neurodevelopmental disorder causing mental retardation. It is caused by mutations in the fragile X mental retardation 1 (fmr1) gene and the absence of the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP). The RNA-binding protein FMRP represses protein translation in synapses, and interacts with the adenosine deaminase acting on the RNA (ADAR) enzyme, which converts adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) and modifies the sequence of RNA transcripts. Utilizing the fmr1 zebrafish mutant (fmr1-/-), we study the link between ADAR-mediated RNA editing, neuronal circuit formation, and behavior in FXS.
The mechanism and treatments of thyroid hormone deficiencies
Thyroid hormones (THs; thyroxine/T4 and triiodothyronine/T3) are key regulators of embryonic development, metabolism, and neurogenesis in all vertebrates. Hypothyroidism is a common pathological condition that is characterized by insufficient activity of THs. In order to function, THs require specific transporter proteins that facilitate their uptake and efflux across the cell membrane, including the monocarboxylate transporter 8 (Mct8) and the organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1C1 (Oatp1c1). The X-linked psychomotor retardation Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome (AHDS) is associated with mutations in the TH monocarboxylate transporter 8 (mct8), and juvenile neurodegeneration is associated with mutation in oatp1c1. We utilize mutants (mct8-/- and oatp1c1-/-), thyroid gland-ablated and additional transgenic zebrafish to elucidate the neurological mechanism and find potential genetic and pharmacological treatments to these TH-related disorders.
Diving, Oxygen Toxicity and brain function
Exposure to high partial pressures of oxygen, which can occur during diving or hyperbaric chamber treatments, may lead to the development of a potentially fatal neurological condition - Central Nervous System Oxygen Toxicity (CNS-OT). CNS-OT is characterized by a loss of consciousness and the onset of seizures similar to tonic-clonic epilepsy. We use live imaging of transgenic zebrafish located inside a hyperbaric chamber, in order to understand the effect of oxygen toxicity on the brain in real time.
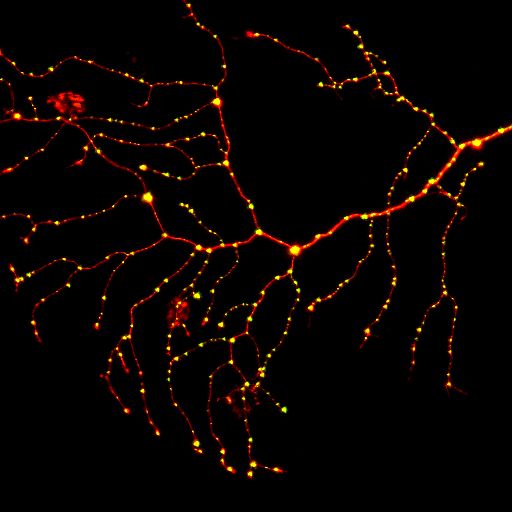
Sensory neuron. Red - Nueron Green(yellow) - Synapses (David Zada)
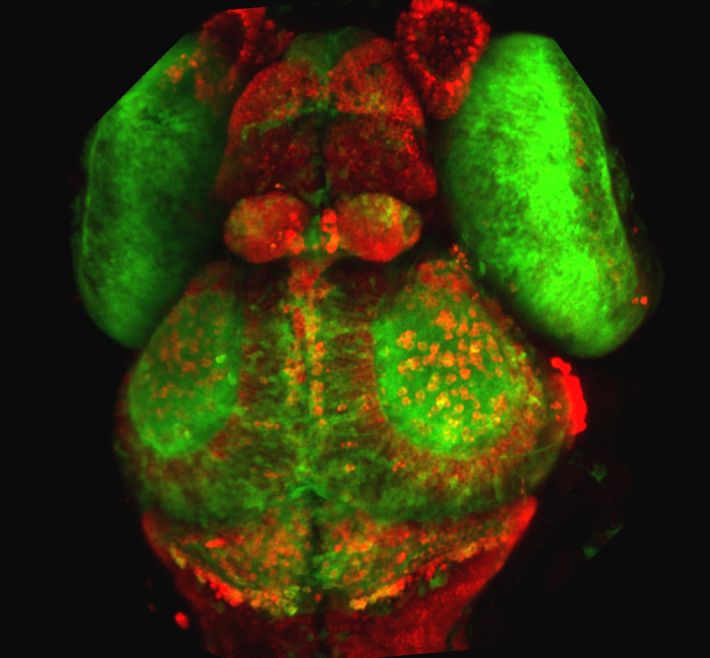
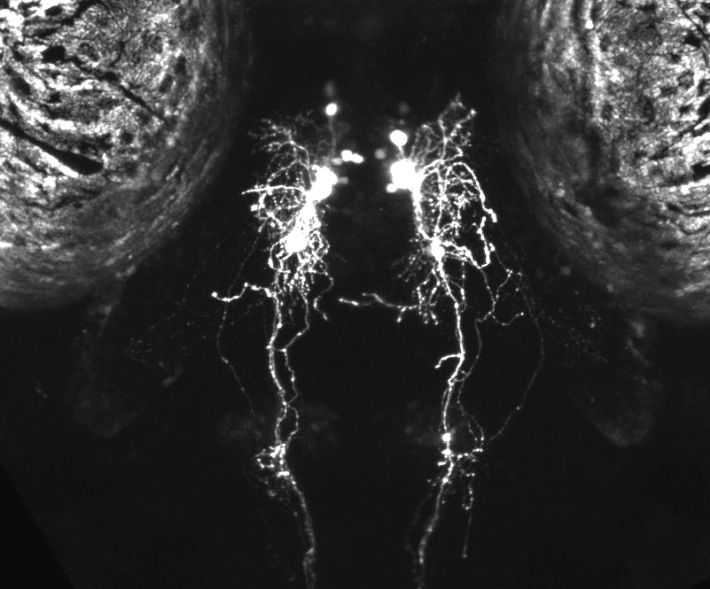
Hypocretin cell in Zebrafish head
Supervision of graduate and post-graduate students
Current
Dr. Yuval Rave - PhD student (2018-present)
Dr. Raphaël Aguillon - Postdoctoral Fellow (CO-PI Prof. Oren Levy, 2019-Present)
Shahaf Ben-Ezra - PhD student (CO-PI Prof. Oren Levy, 2019-Present)
Gali Krayden - MSc and PhD student (2021-present)
Ayelet Hallakoun - MSc and PhD student (2021-present)
Michal Zarfati - MSc student (2023-present)
Shira Leibovitch - MSc student (2023-present)
Lior Gilboa - MSc student (2023-present)
Yuval Fogel - MSc student (2024-present)
Ben Kaz - MSc student (2024-present)
Alumni
Rotem Rozenblat - MSc and PhD student (2017-2024)
Dana Sagi - MSc and PhD student (2017-2024)
Amir Harduf - PhD student (CO-PI Prof. Oren Levy, 2020-2024)
Talya Wasserman - PhD student (2018-2023)
David Zada - PhD and Postdoctoral Fellow (2014-2021)
Daniel Forer - MSc student (2019-2021)
Adir Monsenego - MSc student (2018-2020)
Tali Levitas - PhD student (2014-2019)
Adi Tovin - Postdoctoral Fellow (2012-2016)
Arnon Itiel - MSc student (2013-2017)
Laura Bekerman - PhD student (2010-2015)
Gad Vatine - Postdoctoral Fellow (2010-2012)
Idan Elbaz - MSc and PhD student (2010-2016)
Adi Shamay - MSc and PhD student (2012-2019)
Tali Levitas - MSc student (2012-2014)
David Zada - MSc student (2012-2014)
Inbal Admati - MSc student (2016-2018)
Publications
-
Sagi D, Tibi T, Admati I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Hochgerner H, Zeisel A, Appelbaum L (2024) Single-cell profiling uncovers evolutionary divergence of Hypocretin/Orexin neuronal subpopulations. Journal of Neuroscience https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0095-24.2024
-
Surm JM, Birch S, Macrander J, Jaimes-Becerra A, Fridrich A, Aharoni R, Rozenblat R, Sharabany J, Appelbaum L, Reitzel AM, Moran Y (2024). Venom trade-off shapes interspecific interactions, physiology, and reproduction. Sci. Adv. 10 (11):eadk3870
-
Aguillon R, Rinsky M, Simon-Blecher N, Doniger T, Appelbaum L, Levy O (2024). CLOCK evolved in cnidaria to synchronize internal rhythms with circadian environmental cues. eLife 12:RP89499
-
Uribe-Arias A, Rozenblat R, Vinepinsky E, Marachlian E, Kulkarni A, Zada D, Privat M, Topsakalian D, Charpy S, Candat V, Nourin S, Appelbaum L, Sumbre G (2023). Radial astrocyte synchronization modulates the visual system during behavioral-state transitions. Neuron 111 (24):4040-4057
-
Wasserman-Bartov T, Admati I, Lebenthal-Loinger I, Sharabany J, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2022). Tsh induces Agrp1 neuron proliferation in Oatp1c1 deficient zebrafish. Journal of Neuroscience 42 (44):8214-8224
-
Rozenblat R, Tovin A, Zada D, Lebenthal-Loinger I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2022). Genetic and neurological deficiencies in the visual system of mct8 mutant zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23 (5):2464
-
Confino S, Dor T, Tovin A, Wexler Y, Ben-Moshe Livne Z, Kolker M, Pisanty O, Park SK, Geyer N, Reiter J, Edvardson S, Mor-Shaked H, Elpeleg O, Vallone D, Appelbaum L, Foulkes NS, Gothilf G (2022). A zebrafish model for a rare genetic disease reveals a conserved role for FBXL3 in the circadian clock system. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23 (4):2373
-
Zada D, Sela Y, Matosevich N, Monsonego A, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Nir Y, Appelbaum L (2021). Parp1 promotes sleep, which enhances DNA repair in neurons. Molecular Cell 81:4979-4993
-
Simon-Blecher N, Jacob A, Levy O, Appelbaum L, Elbaz-Ifrah S, Achituv Y (2021). Flatfoot in Africa, the cirripede Chthamalus in the west Indian Ocean. PeerJ. 9:e11710
-
Sagi D, de Lecea L, Appelbaum L (2021). Heterogeneity of Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons. In: The Orexin System. Basic Science and Role in Sleep Pathology. Front Neurol Neurosci. Basel, Karger, 45:61–74
-
Buchumenski I, Holler K, Appelbaum L, Eisenberg E, Junker JP and Levanon EY (2021). Systematic identification of A-to-I RNA editing in zebrafish development and adult organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:4325-4337
-
Blitz E, Matsuda H, Guenther S, Morikawa T, Kubota Y, Zada D, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Stainier DYR, Appelbaum L (2021). Thyroid hormones regulate goblet cell differentiation and Fgf19-Fgfr4 signaling. Endocrinology 162 (5):bqab047
-
Nakajo H, Chou MY, Kinoshita M, Appelbaum L, Shimazaki H, Tsuboi T, Okamoto H (2020). Hunger and the orexin-habenula circuit induces winning in social conflicts. Cell Rep. 31 (12):107790
-
Jaggard J, Lloyd E, Yuiska A, Patch A, Fily Y, Kowalko JE, Appelbaum L, Duboue ER, Keene AC. (2020). Cavefish brain atlases reveal functional and anatomical convergence across independently evolved populations. Sci Adv. 6 (38):eaba3126
-
Keene AC, Appelbaum L (2019). Sleep in Fish Models. In: Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience. Elsevier 30, 363-374
-
Zada D, Appelbaum L (2019). Behavioral criteria and techniques to define sleep in zebrafish. In: Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish. Elsevier 141-153
-
Admati I, Wasserman-Bartov T, Tovin A, Rozenblat R, Rozenblat R, Blitz E, Zada D, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2019). Neural alterations and hyperactivity of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis in Oatp1c1-deficiency. Thyroid 30 (1):161-174
-
Biran J, Gliksberg M, Shirat I, Swaminathan A, Levitas-Djerbi T, Appelbaum L, Levkowitz G (2020). Splice-specific deficiency of the PTSD-associated gene PAC1 leads to a paradoxical age-dependent stress behavior. Scientific Rep. 10 (1):9559
-
Levitas-Djerbi T, Sagi D, Lebenthal-Loinger I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2019). Neurotensin Enhances Locomotor Activity and Arousal, and Inhibits Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Signalings. Neuroendocrinology 110 (1-2):35-49
-
Zada D, Bronshtein I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Garini Y, Appelbaum L (2019). Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons. Nature Communication 10 (1):895
-
Dvir H, Elbaz I, Havlin S, Appelbaum L, Ivanov PC, Bartsch RP (2018). Neuronal noise as an origin of sleep arousals and its role in sudden infant death syndrome. Science Advances 4 (4):eaar6277
-
Eban-Rothschild A, Appelbaum L, de Lecea L (2018). Neuronal Mechanisms for Sleep/Wake Regulation and Modulatory Drive. Neuropsychopharmacology 43 (5):937-952
-
Levitas-Djerbi T, Appelbaum L (2017). Modeling sleep and neuropsychiatric disorders in zebrafish. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 44:89-93
-
Zada D, Blitz E, Appelbaum L (2017). Zebrafish - An emerging model to explore thyroid hormone transporters and psychomotor retardation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 459:53-58
-
Elbaz I, Levitas-Djerbi T, Appelbaum L (2016). The Hypocretin/Orexin Neuronal Networks in Zebrafish. Curr Topics Behav Neurosci. 33:75-92
-
Elbaz I, Zada D, Tovin A, Braun T, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Wang G, Mourrain P, Appelbaum L (2016). Sleep-Dependent Structural Synaptic Plasticity of Inhibitory Synapses in the Dendrites of Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 54 (8): 6581-6597
-
Zada D, Tovin A, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2016). Pharmacological and BBB-targeted genetic therapies for thyroid hormone-dependent hypomyelination. Disease Models & Mechanisms. 9 (11):1339-1348
-
Shamay-Ramot A, Khermesh K, Porath HT, Barak M, Pinto Y, Wachtel C, Zilberberg A, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Efroni S, Levanon EY, Appelbaum L (2015). Fmrp interacts with Adar and regulates RNA editing, synaptic density and locomotor activity in zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 11 (12):e1005702.
-
Yelin-Bekerman L, Elbaz I, Diber A, Dahary D, Gibbs-Bar L, Alon S, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2015). Hypocretin neuron-specific transcriptome profiling identifies the sleep modulator Kcnh4a. Elife 4: e08638
-
Oren M, Tarrant AM, Alon S, Simon-Blecher N, Elbaz I, Appelbaum L, Levy O (2015). Profiling molecular and behavioral circadian rhythms in the non-symbiotic sea anemone Nematostella vectensis. Scientific reports 5:11418
-
Levitas-Djerbi T, Yelin-Bekerman L, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Appelbaum L (2015). The Hypothalamic Leptin-Neurotensin-Hypocretin Neuronal Networks in Zebrafish. J Comp Neurol. 523:831-848
-
Elbaz I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Okamoto H, Appelbaum L (2015). Reduced synaptic density and deficient locomotor response in neuronal activity-regulated pentraxin 2a mutant zebrafish. FASEB J. 29:1220-34
-
Zada D, Tovin A, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Vatine GD, Appelbaum L (2014). Altered behavioral performance and live imaging of circuit-specific neural deficiencies in a zebrafish model for psychomotor retardation. PLoS Genet. 10 (9):e1004615
-
Sharaby Y, Lahmi R, Amar O, Elbaz I, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Weiss AM, Appelbaum L, Tzur A (2014). Gas2l3 is essential for brain morphogenesis and development. Dev Biol. 394:305-13
-
Oren M, Brikner I, Appelbaum L, Levy O (2014). Fast neurotransmission related genes are expressed in non nervous endoderm in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis. PLoS One. 9:e93832
-
Elbaz I, Foulkes NS, Gothilf Y, Appelbaum L (2013). Circadian clocks, rhythmic synaptic plasticity and the sleep-wake cycle in zebrafish. Frontiers in Neural Circuits 7:9
-
Vatine G, Zada D, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Tovin A, Malkinson G, Yaniv K, Appelbaum L (2013). Zebrafish as a model for monocarboxyl transporter 8-deficiency. J Biol Chem 288 (1):169-180
-
Elbaz I, Yelin-Bekerman L, Nicenboim J, Vatine G, Appelbaum L (2012). Genetic ablation of hypocretin neurons alters behavioral state transitions in zebrafish. The Journal of Neuroscience 32 (37):12961-72
-
Wang G, Grone B, Colas D, Appelbaum L, Mourrain P (2011). Synaptic plasticity in sleep: learning, homeostasis and disease. Trends in Neurosciences 34 (9):452-63
-
Appelbaum L, Wang G, Yokogawa T, Skariah G, Smith SJ, Mourrain P and Mignot E (2010). Circadian and homeostatic regulation of structural synaptic plasticity in hypocretin neurons. Neuron 68 (1):87-98 (cover)*. *This paper was highlighted in Nature: Neuroscience: Brain connections have rhythm. Nature 468:349
-
Appelbaum L, Wang G, Maro G, Mori R, Tovin A, Marin W, Yokogawa Y, Kawakami K, Smith SJ, Gothilf Y, Mignot EM and Mourrain P (2009). Sleep/wake regulation and hypocretin-melatonin interaction in zebrafish. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 106 (51):21942-7 (track II)
-
Vatine G, Vallone D, Appelbaum L, Mracek P, Ben-Moshe Z, Lahiri K, Gothilf Y and Foulkes NS (2009). Light directs zebrafish period2 expression via conserved D and E boxes. PLoS Biol. 7 (10):e1000223
-
Levy O, Appelbaum L, Leggat W, Gothlif Y, Hayward DC, Miller DJ and Hoegh-Guldberg O (2007). Light-responsive cryptochromes from the simplest marine eumetazoan animals. Science 318 (5849):467-470
-
Yokogawa T, Marin W, Faraco J, Pezeron G, Appelbaum L, Zhang J, Rosa F, Mourrain P and Mignot E (2007). Characterization of sleep in zebrafish and insomnia in hypocretin receptor mutants. PLoS Biology 5 (10):e277
-
Appelbaum L, Skariah G, Mourrain P and Mignot E (2007). Purinergic transmission by P2X receptors and ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 in hypocretin and sensory neurons in zebrafish. Brain Res. 1174:66-75
-
Zilberman-Peled* B, Appelbaum* L, Vallone D, Foulkes NS, Anava S, Anzulovich A, Coon SL, Klein DC, Falcon J, Ron B and Gothilf Y (2007).Transcriptional regulation of arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase-2 gene in the pineal gland of the gilthead seabream. Journal of Neuroendocrinology 19:46-53 *Equally contributed.
-
Faraco* JH, Appelbaum* L, Marin W, Gaus S, Mourrain P, Mignot E (2006). Regulation of hypocretin (orexin) expression in embryonic zebrafish. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281:29753-61 *Equally contributed
-
Appelbaum L, Gothilf Y (2006). Mechanism of pineal-specific gene expression: The role of E-box and photoreceptor conserved elements. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 252 (1-2):27-33
-
Appelbaum L, Vallone D, Anzulovich A, Ziv L, Tom M, Foulkes N, Gothilf Y (2006). Zebrafish arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase genes - targets for regulation of circadian-clock. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 36 (2):337-347
-
Appelbaum L, Anzulovich A, Baler R, Gothilf Y (2005). Homeobox-clock protein interaction in zebrafish: A shared mechanism for pineal-specific and circadian gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280 (12):11544–11551
-
Appelbaum L, Toyama R, Dawid IB, Klein DC, Baler R, Gothilf Y (2004). Zebrafish serotonin-N-acetyltransferase-2 gene regulation: Pineal-restrictive downstream module (PRDM) contains a functional E-box and three photoreceptor conserved elements. Molecular Endocrinology 18 (5):1210-1221
-
Appelbaum L, Achituv Y, Mokady O (2002). Speciation and the establishment of zonation in an intertidal barnacle - specific settlement versus selection. Molecular Ecology 11 (9):1731-1737
Last Updated Date : 01/04/2025